This week, we will discuss how the CONFIDENCE trial gets nephrology closer to the magic CKD polypill of CKD.
CONFIDENCE Visual Abstract
Check out the beautiful visual abstract made by NephJC intern Michelle Fravel.
Resumen Visual Ensayo CONFIDENCE
El ensayo CONFIDENCE evaluó la combinación de finerenona + empagliflozina en ERC + DM2: mayor reducción de CACu a 180 días. ¿Estamos listos para iniciar la terapia combinada desde el principio?
Revisa el resumen visual por Michelle Fravel
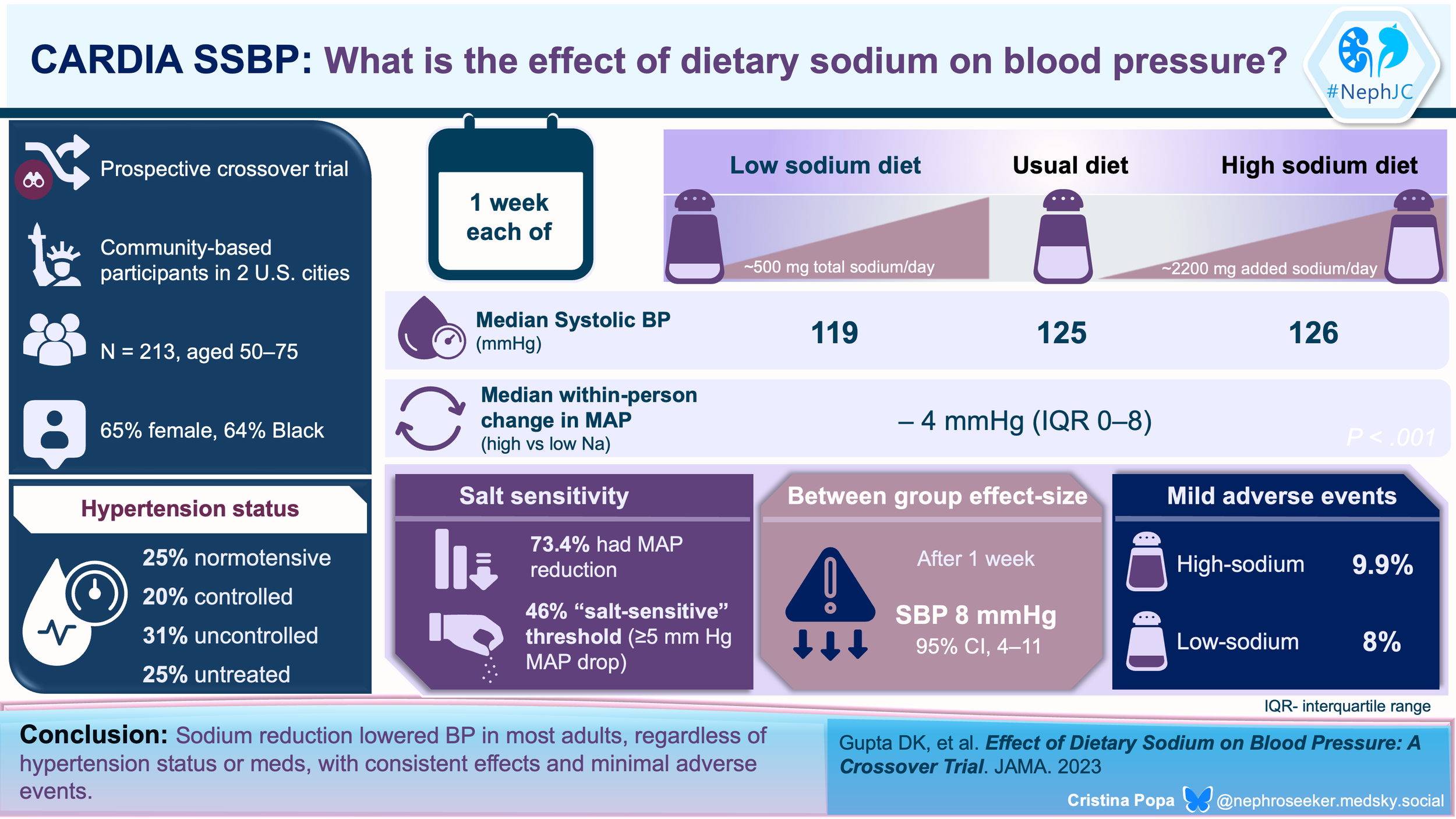
NephJC Shorts: Salt reduction still lowers BP
JAMA 2023 Dec 19;330(23):2258-2266
doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.23651.
Effect of Dietary Sodium on Blood Pressure: A Crossover Trial
Deepak K Gupta, Cora E Lewis, Krista A Varady, Yan Ru Su, Meena S Madhur, Daniel T Lackland, Jared P Reis, Thomas J Wang, Donald M Lloyd-Jones, Norrina B Allen
PMID: 37950918
We know reducing sodium intake lowers blood pressure (BP), but what is truly the effect in those with normal BP versus high BP? Those taking BP meds versus those who do not? In the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA)–SSBP trial (Gupta et al, JAMA 2023), the investigators enrolled 213 individuals either with normal BP or not, and either on BP meds with controlled or uncontrolled hypertension. They crossed over from the usual diet to low sodium (diet with 500 mg i.e. ~ 25 mmol sodium) and high sodium (with 2 bouillon packets, each containing 1100 mg of sodium added to the usual diet). The low sodium diet did result in lower BP in all subgroups, by about 5 - 6 mmHg SBP in the normotensive/controlled hypertension subgroups to about 9 - 190 mmHg SBP in the uncontrolled/untreated hypertension subgroups.
Figure 2 from Gupta et al, JAMA 2023. Distributions of Within-Individual 24-Hour Ambulatory BP Response to Dietary Sodium Intake, Calculated From High-Sodium Diet Minus Low-Sodium Diet
Though the authors say these are not significantly different based on interaction p values, the subgroups are woefully underpowered to say that. Note that diet allocation was on alternate days, so this was not a randomized trial. Additionally - despite being provided food and daily phone calls, people on low sodium couldn’t stick to the provided saltless diet (24 hour urine sodium 1.7g rather than 0.5 g) and even the high sodium group couldn’t stomach the extra 2.2g bouillon (24 hour urine sodium went up from 4.6 to 5.5 rather than expected 6.8 g/day). So, an extremely low sodium diet does lower BP a bit, but it’s hard to achieve even if you are provided the food. Salt substitutes are so much more pragmatic (NephJC Summary| Podcast)!
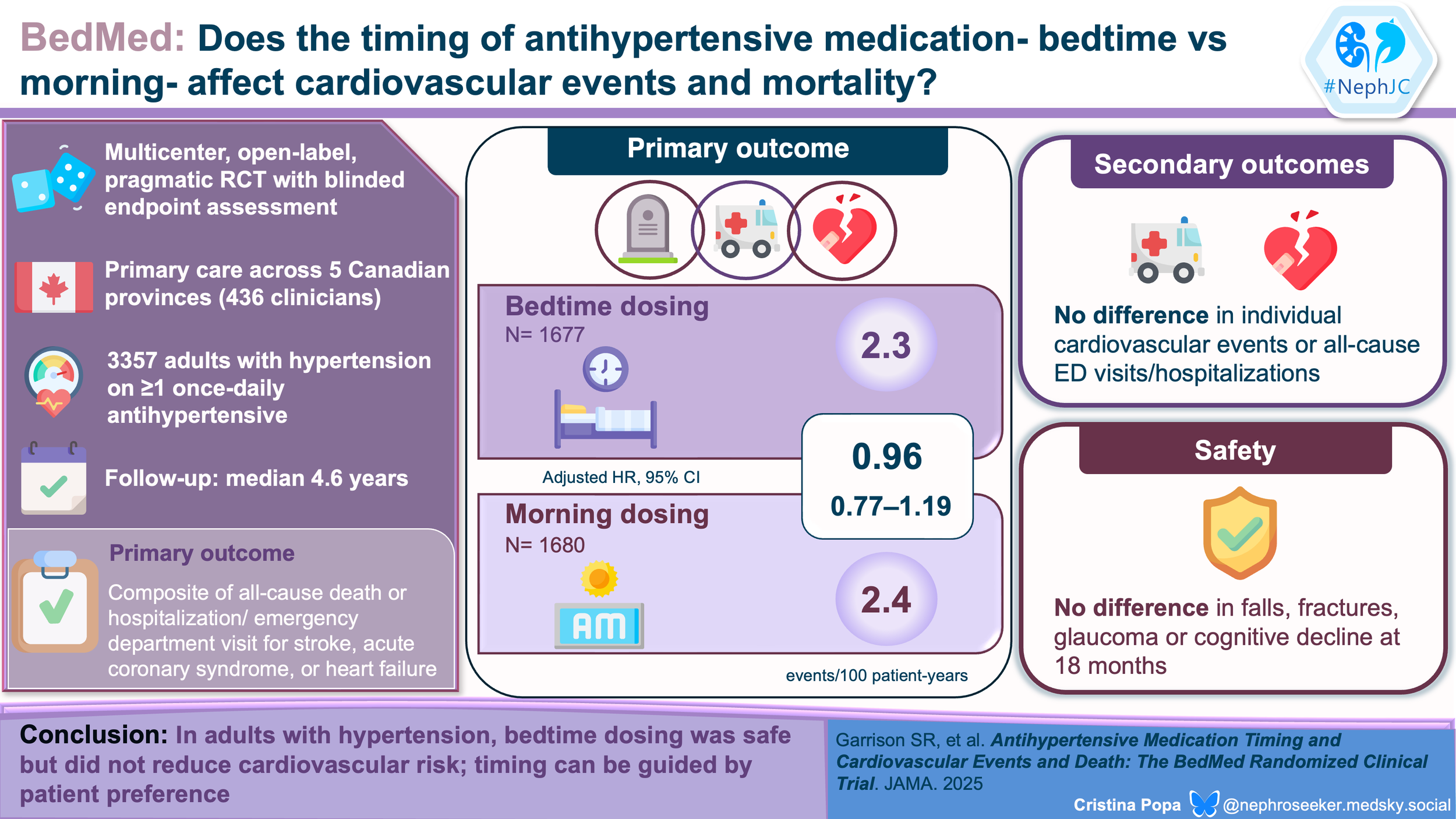
NephJC Shorts: BedMed and Chronotherapy
Introducing NephJC Shorts
In just over a decade of critical appraisal on NephJC, we have done several experiments. Some of them have worked out phenomenally well, such as the Freely Filtered podcast. Others were not ready for the time, such as the Google Hangouts. We want to try another such experiment, and hope we receive feedback to decide if this is something worthwhile that we should continue doing.
There are many studies and many trials and many reviews, and many guidelines that are published in Nephrology every week. Indeed, it is a golden era for randomized controlled trials in Nephrology. On the other hand, NephJC only occurs twice a month. It does take a lot of work, with the detailed critical appraisal, readable summary, visual, abstracts, and the chats. Sometimes the occasional, irregularly irregular podcast. Hence, we cannot deal with all the worthwhile studies that are coming out.
Enter NephJC Shorts.
This week, we are publishing a few short blogs. The purpose here is to cover some notable studies in brief. They do not receive the full, long, NephJC treatment. The articles we choose are those that the NephJC editorial team fancies, but suggestions are welcome. Since these are a shorter format, we don’t do a deep dive into the methods and don’t have a long list of the limitations and strengths. Think of them as a pithy version of the usual NephJC blog. Feedback welcome!
The NephJC Editors
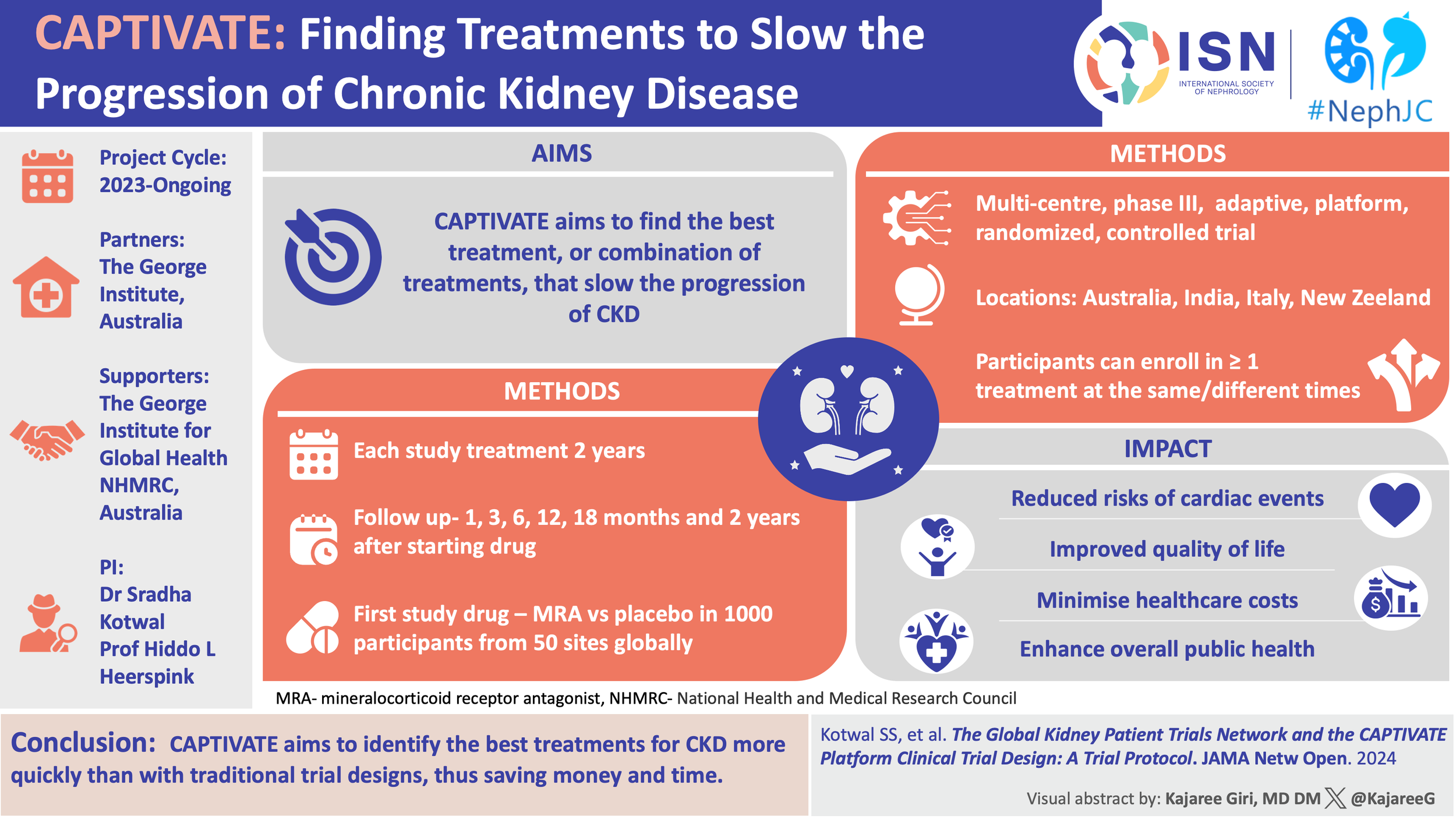
CAPTIVATE NephTrials Visual Abstract
Check out the beautiful visual abstract made by Kajaree Giri
Do nudges increase the use of GDMT in diabetic CKD?
Is tacrolimus superior to MMF in pediatric steroid sensitive nephrotic syndrome?
From single shots to strategy: How CAPTIVATE is reframing the NephTrials playbook
Ensayo NUDGE-CKD: El Resumen Visual
El estudio NUDGE-CKD evaluó si enviar cartas electrónicas con recomendaciones a médicos y pacientes podía aumentar el uso de tratamientos clave en enfermedad renal crónica (iSRAA o iSGLT2).
Revisa el resumen visual por Divya Bajpal
¿El resultado? Hoy en vivo por #NephJC!
The NUDGE-CKD Visual Abstract
Check out the beautiful visual abstract made by NephJC faculty Dr Divyia Bajpai
Are E-Nudges Enough to Push Guideline-Based CKD Therapy?
NephJC Internship Reforms and then Reforms
NephJC Bookclub returns on August 19th
Here at NephJC we know that the summer is a hard time to focus on medical minutia, it is a time to find a comfortable chair and lose yourself in a book so for the 11th year we are doing a book rather than journal club chat. This summer our community is going to read John Green’s Everything is Tuberculosis.
Book homepage: EverythingIsTB.com
Ensayo STAMP: ¿Tacrolimus o Micofenolato en el síndrome nefrótico pediátrico?
El síndrome nefrótico en niños puede implicar recaídas frecuentes, alta carga de esteroides y decisiones terapéuticas difíciles. Entonces, ¿cuál mantiene mejor la remisión: tacrolimus o micofenolato de mofetilo?
Revisa el VA y únete a la discusión en #NephJC
The STAMP Trial VA: Who Gets the Approval—TAC or MMF in Pediatric Nephrotic Syndrome?
Nephrotic syndrome in kids can mean frequent relapses, high steroid burden, and tough treatment choices. So which helps maintain remission better: Tacrolimus or MMF?
See the Visual Abstract Krithika Mohan
¿TAC o MMF en el síndrome nefrótico pediátrico?
El ensayo STAMP comparó ambos tratamientos en niños con recaídas frecuentes o corticodependencia.
¿Cuál fue más eficaz? ¿Qué tan seguros son?
🖼️ Revisa el VA completo #NephJC
TAC or MMF—what works better in pediatric nephrotic syndrome?
Nephrotic syndrome in children, especially those with frequent relapses or steroid dependence, remains a therapeutic challenge. The STAMP trial compared tacrolimus and mycophenolate mofetil to help guide treatment decisions.